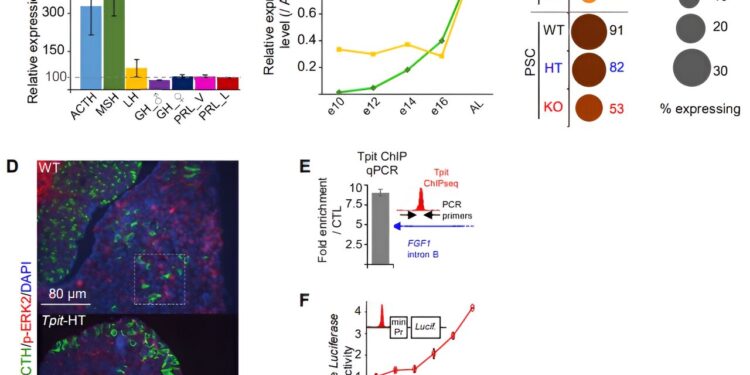
Tpit regulates the expression of corticotropin- and corticotropin-melanotropin-specific genes. Credit: Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (2024). DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2410269121
Researchers led by Jacques Drouin and his team at the IRCM have discovered an intercellular communication mechanism at the origin of the balance of hormones necessary to maintain a healthy human.
Hormonal balance is essential for the proper functioning of the human body. A disruption in this balance can lead to many health problems, such as metabolic syndrome and obesity.
Today, a new international study led by scientists from the Montreal Clinical Research Institute (IRCM), affiliated with the University of Montreal, sheds light on an important element of the mechanisms underlying this balance.
“We want to understand how the exchange of signals between cells modulates gene expression, and how their disruption causes disease,” explains the study’s lead author, Jacques Drouin, director of the IRCM’s molecular genetics research unit.
The pituitary gland plays a vital role in maintaining a person’s hormonal balance, as it produces the main hormones that control the other glands. In the pituitary gland, the different hormone-producing cells communicate with each other via dedicated ligands and receptors to balance the production of different hormones.
However, little is known about these ligands, and it is precisely one of them that Drouin, professor in the Department of Biochemistry at UdeM, identified in his laboratory at the IRCM as part of the study.
Published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of SciencesThe multidisciplinary study also involved researchers from France (Institute of Functional Genomics, Montpellier) and the United Kingdom (University of Edinburgh and University of Oxford).
They helped Drouin’s team uncover a mechanism for communication between two types of cells within the pituitary gland, discovering that pituitary cells that regulate stress “talk” to neighboring cells that secrete growth hormone.
The researchers discovered that this FGF1-mediated communication is essential for normal growth because this factor controls the number and function of growth hormone-producing cells.
The study illustrates the functional importance of intercellular signaling, but it’s just the beginning, the researchers say. There are many more, including the exchanges between hormone-producing cells and their progenitors.
The balance between all these cells is the basis of a harmonious organism.
More information:
Konstantin Khetchoumian et al, Paracrine FGF1 signaling directs pituitary architecture and size, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (2024). DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2410269121
Provided by the University of Montreal
Quote: Researchers discover intercellular communication mechanism behind hormonal balance (2024, September 26) retrieved September 26, 2024 from
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no part may be reproduced without written permission. The content is provided for informational purposes only.