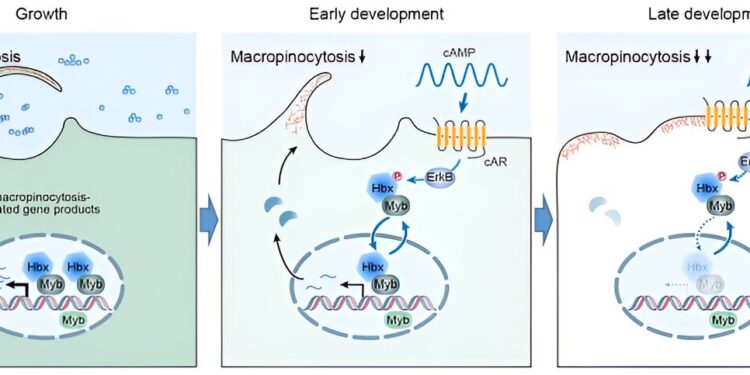
The Hbx5-MybG transcription factor complex enables adaptive changes in macropinocytosis during the growth-development transition. Credit: Cai Huaqing’s group
Macropinocytosis is one of the major pathways by which cells nonselectively internalize extracellular fluids. The laboratory strain Dictyostelium discoideum constitutes a valuable model for studying the regulation of macropinocytosis.
This model cell is a social amoeba that exists as a single cell when nutrients are abundant and uses macropinocytosis to acquire nutrients. Under conditions of nutrient deprivation, it enters a developmental phase and undergoes directed migration to form multicellular structures. The molecular mechanisms underlying this transition from macropinocytosis to migration mode still remain unclear.
In a study published in Development cell On February 6, researchers led by Professor Cai Huaqing of the Institute of Biophysics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, together with Professor Li Lei of Peking University, revealed the molecular mechanisms by which cells regulate the level of macropinocytosis in response to nutrients. stress.
Using advanced genetic screening and mass spectrometry, the researchers first identified two transcription factors, Hbx5 and MybG, involved in macropinocytosis.
Using microscopy, biochemical experiments, RNA-Seq and ChIP-Seq, the researchers discovered that Hbx5 and MybG form a heterodimeric complex. During the nutrient growth phase, this complex localizes in the cell nucleus and regulates the expression of genes involved in macropinocytosis, thereby maintaining high levels of macropinocytosis.
Under nutritional stress, oscillatory cAMP signaling causes nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of the Hbx5-MybG complex, leading to downregulation of genes involved in macropinocytosis. As the frequency of oscillatory cAMP signaling increases during development, the Hbx5-MybG complex stops shuttling and becomes trapped in the cytoplasm, turning off the expression of genes promoting macropinocytosis and facilitating the transition to a directed migration behavior.
This study identified key regulatory components that allow cells to maintain macropinocytosis and modulate its level in response to nutritional stress. This not only provides new insights into the molecular mechanisms by which cells regulate macropinocytosis in response to environmental changes, but also opens new avenues to study the mechanisms of decoding oscillatory signaling in cells.
More information:
Yazhou Hao et al, A transcription factor complex in Dictyostelium enables adaptive changes in macropinocytosis during the growth-development transition, Development cell (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2024.01.012
Provided by the Chinese Academy of Sciences
Quote: Researchers discover how cells modulate macropinocyte activity (February 21, 2024) retrieved February 21, 2024 from
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from fair use for private study or research purposes, no part may be reproduced without written permission. The content is provided for information only.