Graphic summary. Credit: iScience (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.110413
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is a fast-growing, highly malignant subtype of lung cancer. One of the biggest challenges doctors face is the cancer’s resistance to platinum-based chemotherapy, the standard treatment for patients with SCLC.
Recently, a research group led by Professor Hong Bo from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, identified a novel prognostic biomarker that could help predict chemotherapy resistance in SCLC through integrative multi-omics analysis.
This discovery, published in iSciencecould improve treatments for this aggressive form of cancer.
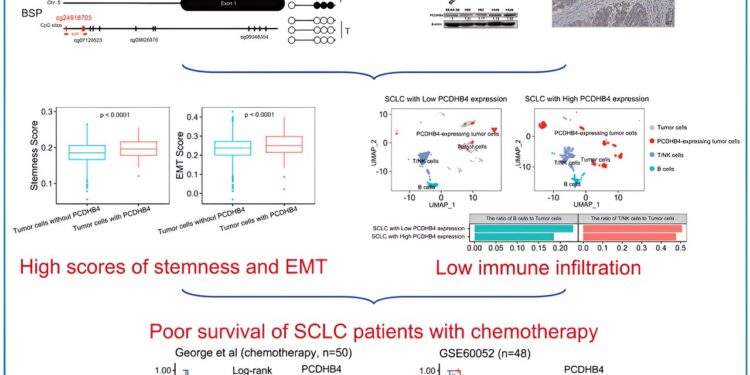
In this study, researchers conducted an integrative analysis of transcriptome and methylome data, revealing a strong correlation between high PCDHB4 gene expression and poor survival in SCLC patients treated with chemotherapy.
Further research using clinical samples and cell lines confirmed that the PCDHB4 gene had lower methylation levels and was more active in SCLC, contributing to the cancer’s resistance to chemotherapy.
Analysis of bulk and single-cell RNA sequencing data indicated that SCLC tumors with high PCDHB4 expression were associated with lower immune infiltration and higher stemness and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) scores.
This study highlighted PCDHB4 as a key biomarker that could help predict which patients are more likely to develop resistance to chemotherapy, the team said.
More information:
Qizhi Zhu et al, Integration of transcriptome and methylome related to cisplatin resistance identifies PCDHB4 as a novel prognostic biomarker in small cell lung cancer, iScience (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.110413
Provided by Chinese Academy of Sciences
Quote:Novel prognostic biomarker identified in small cell lung cancer (2024, August 26) retrieved August 26, 2024 from
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no part may be reproduced without written permission. The content is provided for informational purposes only.