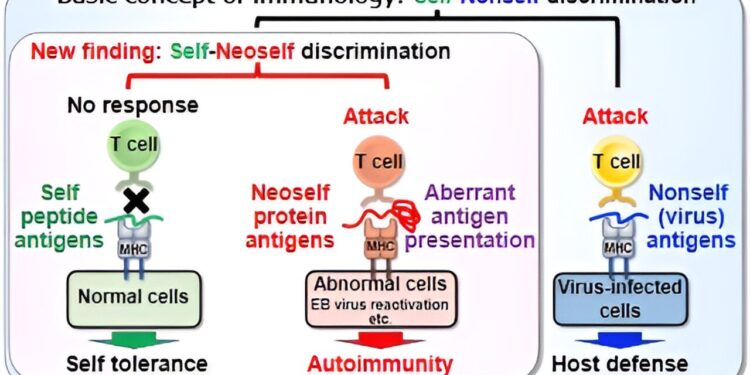
Research Summary: This study found that T cells can distinguish between self and neo-self antigens, and that neo-self-reactive T cells are involved in the development of autoimmune diseases. Credit: Hisashi Arase, Osaka University
Autoimmune diseases are widespread and notoriously difficult to treat. This is partly because why the immune system attacks its own tissues in patients with these diseases remains poorly understood.
In a study published in CellResearchers at Osaka University have revealed that the body’s own proteins with an unusual structure trigger a wave of inflammation in immune cells that leads to autoimmunity. The article is titled “Self-antigens are the primary target of autoreactive T cells in human lupus.”
Autoimmune diseases develop when the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own tissues instead of fighting foreign invaders like bacteria or viruses. However, why this happens has long remained a mystery, as the immune system has many checks and balances to ensure that it only responds to “non-self” triggers.
“T cells are thought to distinguish between small protein fragments derived from self and non-self proteins displayed on the major histocompatibility complex II (MHC-II), and are ‘trained’ not to respond to self antigens,” said the study’s lead author, Hisashi Arase.
“However, when MHC-II lacks a crucial element called the invariant chain (Ii), it can present larger, misfolded self-antigens, called neo-self-antigens, to T cells.”
Since autoantibodies to neo-self-antigens are frequently found in patients with autoimmune diseases, the researchers studied T-cell reactivity in lupus patients and in mice, in which Ii was depleted in adults. They also studied the effect of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection, a risk factor for lupus, on T-cell reactivity to neo-self-antigens.
“The results were striking,” says Shunsuke Mori, lead author. “We found that about 10% of the clonally expanded T cell repertoire in lupus patients recognized the neo-autoantigens. Moreover, the induction of neo-autoantigens induced lupus-like disease in the mice, meaning they mounted an immune response against the body’s own tissues, causing an autoimmune disease.”
In addition, the researchers found that reactivation of EBV, which most people are infected with but is usually dormant, increases the presentation of neo-self antigens on MHC-II by downregulating the expression of Ii virus, triggering the activation of T cells directed against the organism. This could explain why reactivation of EBV is linked to the onset or exacerbation of lupus.
“Our results demonstrate that T cells distinguish between self-antigens and neo-self-antigens and do not recognize neo-self-antigens as self-antigens, thereby leading to the development of autoimmunity when neo-self-antigens are presented on MHC-II,” Arase explains.
This study significantly advances our understanding of T cell self-tolerance and the causes of autoimmune diseases by identifying neo-autoantigens as a distinct class of antigens that trigger an inappropriate immune response. This understanding of why the body begins to attack itself could help develop new treatments for autoimmune diseases like lupus.
More information:
Neo-autoantigens are the primary target of autoreactive T cells in human lupus, Cell (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2024.08.025. www.cell.com/cell/fulltext/S0092-8674(24)00913-9
Cell
Provided by Osaka University
Quote: Neo-autoimmune antigens induce autoimmune response in lupus (2024, September 13) retrieved September 13, 2024 from
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no part may be reproduced without written permission. The content is provided for informational purposes only.