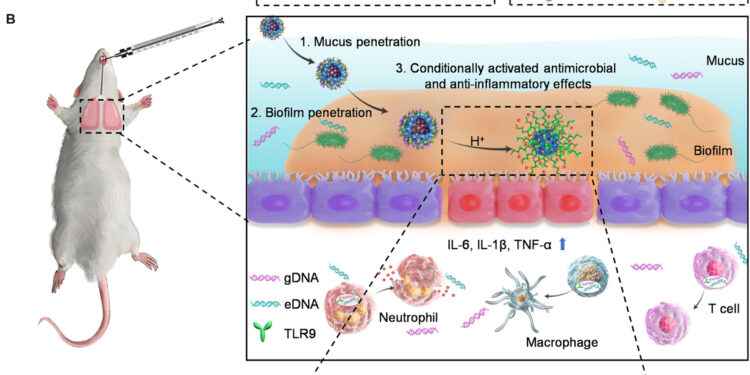
Schematic illustration of IMAMs penetrating mucus and biofilm for immunoantibacterial treatment of COPD. (A) A diagram illustrating the construction of IMAM (MEKCalifornia/CAZ NP). (B) A schematic illustrating IMAMs penetrating mucus and biofilm, followed by charge/conformation transformation in the acidic environment. MEKCalifornia NPs act synergistically with CAZ to eliminate bacterial infections, eliminate eDNA and gDNA, avoid excessive activation of immune cells, and ultimately achieve antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effects. TFA, trifluoroacetic acid; IL-6, interleukin-6; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α. Credit: Scientists progress (2024). DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abd7904
A team of nanochemists from Soochow University, China, in collaboration with a colleague from Columbia University, USA, have developed an inhalable antibacterial therapy carried by nanoparticles to treat COPD patients. Their article is published in the journal Scientists progress.
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a condition in which the airways in the lungs become progressively narrower and harder, leading to obstruction of airflow. This also leads to the creation of mucus, which tends to build up. Such accumulations often lead to bacterial infections.
Over the years, scientists have developed a multitude of therapies to treat the symptoms that accompany COPD – the disease itself is considered incurable. These therapies target the symptoms of cough, itching or burning lungs, and inflammation. And while many such therapies offer some degree of relief, few offer effective treatment for bacterial infections. Indeed, antibiotics must pass through both a layer of mucus and the biofilms created by bacteria. In this new effort, the research team created a therapy that could solve this problem.
To kill bacteria in the lungs, a drug must be able to access them directly. The team started with a drug known to kill the types of bacteria that infect the lungs. They then encapsulated it in a hollow silica-based nanoparticle composed of a negatively charged polypeptide. This protected the antibiotic agent as it passed through the mucus. The nanoparticle then made its way through the biofilms via reactions between the polypeptide and the biofilm’s acids, allowing it to fight bacteria on the other side.
The team first tested their approach using cells in a petri dish. Having succeeded, they tested it with mouse models and found that it was able to both effectively fight bacteria and calm the immune response, leading to a reduction in inflammation. The researchers acknowledge that more testing is needed, but also suggest that their technique holds promise for a paradigm shift in the management of COPD.
More information:
Junliang Zhu et al, Inhaled immunoantimicrobials for the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, Scientists progress (2024). DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abd7904
© 2024 Science X Network
Quote: Antibacterial agent carried by nanoparticles used to treat COPD in mice (February 13, 2024) retrieved on February 13, 2024 from
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from fair use for private study or research purposes, no part may be reproduced without written permission. The content is provided for information only.