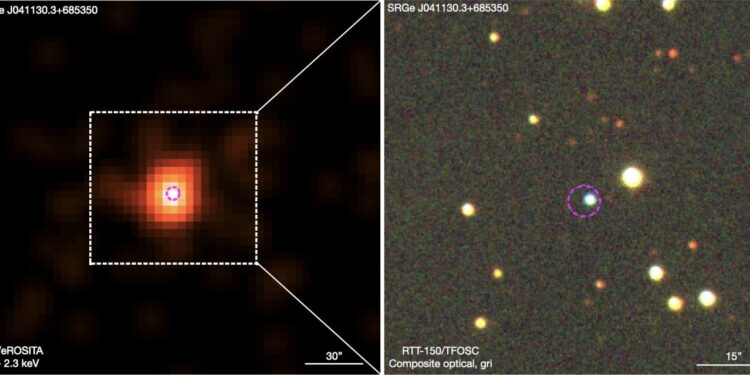
Left: False-color X-ray image of SRGeJ0411 in the 0.3 to 2.3 keV energy band from combined data from four SRG/eROSITA sky surveys. The image was smoothed with a 15” Gaussian kernel. The white box shows the field of view of the optical image on the right. Right: Composite optical image around SRGeJ0411 based on RTT-150/TFOSC data. A pseudo-color image was composed using 𝑔𝑟 𝑖 filters. The magenta circle with a radius of 3.3” (98% localization error, R98) is centered on the radiological position of SRGeJ0411. Credit: Galiullin et al., 2024.
An international team of astronomers reports the discovery of a new cataclysmic variable. The new system, designated SRGeJ041130.3+685350 (or SRGeJ0411 for short), has an orbital period of about 100 minutes and may contain a brown dwarf. The results were detailed in an article published on January 4 in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
Cataclysmic variables (CVs) are binary star systems consisting of a primary white dwarf that accumulates material from a normal companion star. Their brightness increases irregularly and considerably, then falls back to a resting state. These binaries have been found in many environments, such as the center of the Milky Way, the solar neighborhood, and within open and globular clusters.
Now, a group of astronomers led by Ilkham Galiullin of Kazan Federal University in Russia has discovered a new CV as part of a joint SRG/eROSITA and Zwicky Transient Facility (ZTF) program. This multi-wavelength campaign, combining radiological and optical information, makes it possible to search and discover new systems of this type.
“In this paper, we present the study and characterization of the new eclipsing CV with evidence for a secondary brown dwarf, SRGeJ0411,” the researchers wrote.
SRGeJ0411 was discovered during the SRG/eROSITA total sky survey and was identified as a CV candidate due to its high X-ray to optical flow ratio at a level of 0.6. Its optical spectrum shows prominent hydrogen and helium emission lines, typical of cataclysmic variables.
The observation revealed that SRGeJ0411 has an . The ZTF optical light curve shows deep eclipses of the system and provides no evidence of a significant outburst.
According to the study, SRGeJ0411 is located at a distance of approximately 1,056 light years and has an orbital period of 97.53 minutes. The system’s white dwarf is only one percent the size of the sun, while its mass is estimated at 0.84 solar masses. The temperature of the white dwarf was measured at 13,790 K.
Regarding the donor SRGeJ0411, the authors of the article assume that it is a brown dwarf. The object has a radius of less than 0.11 solar radii, a mass of less than 0.04 solar masses, and its temperature is estimated to be less than 1,800 K.
The researchers say SRGeJ0411’s parameters suggest it is a new “rules bouncer.” So-called period bouncers are highly evolved CVs that have passed the minimum orbital period (70 minutes) and are reevolving towards longer orbital periods. Observations show that the donors of empty periods are brown dwarfs.
Therefore, summing up the results, the astronomers concluded that SRGeJ0411 is most likely an eclipse-period bouncer CV system, but further studies are needed to confirm this.
Correction note (01/16/2024): The original story stated that the system’s white dwarf was the size of the sun, which is incorrect. The revised sentence states that the white dwarf is 0.01 times the size of the sun.
More information:
Ilkham Galiullin et al., A joint SRG/eROSITA + ZTF research: Discovery of a cataclysmic eclipsing variable with a period of 97 minutes with evidence of a secondary brown dwarf, Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society (2024). DOI: 10.1093/mnras/stae012. On arXiv: DOI: 10.48550/arxiv.2401.04178
© 2024 Science X Network
Quote: Discovery of a new cataclysmic variable that may contain a secondary brown dwarf (January 16, 2024) retrieved January 16, 2024 from
This document is subject to copyright. Except for fair use for private study or research purposes, no part may be reproduced without written permission. The content is provided for information only.