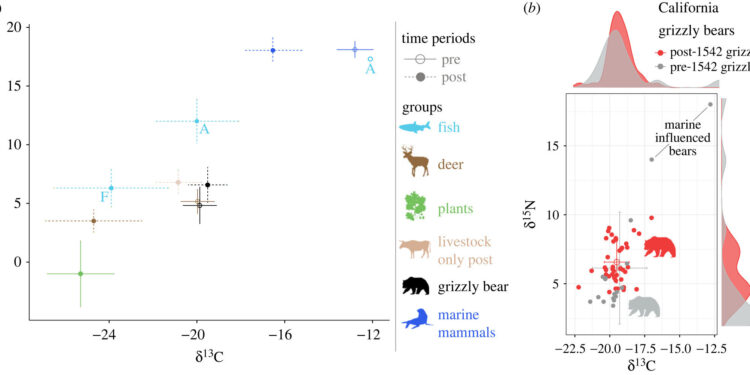
(a) Biplot showing stable isotope values for California grizzly bears and their potential foods statewide during the before and after periods. (b) Biplot showing individual grizzly bears in the pre (gray) and post (red) 1542 periods. Credit: Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences (2024). DOI: 10.1098/rspb.2023.0921
A team of biologists, historians, and earth and environmental scientists affiliated with several institutions in the United States has found evidence that contradicts historical accounts about the size and feeding habits of the California grizzly bear today. now disappeared. In their project, reported in the journal Proceedings of the Royal Society BThe group studied preserved bones and skins of California grizzly bears and compared their results with historical records.
The California grizzly bear (a subspecies of brown bear) lived in many areas of California when European settlers arrived. Over time, bears gained a reputation as massive beasts, some weighing up to 1,000 kilograms, capable of attacking humans and preying on livestock. Their reputation led settlers to hunt them to extinction. The last known California grizzly bear was documented in 1924. In this new effort, the research team investigated whether the California grizzly bear’s reputation was justified.
The work involved testing bones and skins preserved by individuals, groups and museums in two ways. The first was to study the nitrogen and carbon isotopes present in the remains to learn more about the bears’ diet. They found that the bears were mostly vegetarians, both before and after the arrival of the settlers: their diet was generally only 9% meat. The team then measured the size of the bones and pelts and determined that the average weight of the bears was about 200 kg, which they said is close to the average weight of grizzly bears currently living in other regions of the world. ‘North America.
Researchers note that some grizzly bears began eating more meat, especially livestock, after European settlers arrived, encroaching on their territory. But even then, meat still made up only a quarter of their diet. They conclude that the problems created by the California grizzly bear were probably inflated by settlers and hunters who sought to make a name for themselves by tracking and killing the bears and mounting the larger specimens.
More information:
Alexis M. Mychajliw et al, Coupled social and ecological changes led to the historic extinction of the California grizzly bear (Ursus arctos californicus), Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences (2024). DOI: 10.1098/rspb.2023.0921
© 2024 Science X Network
Quote: California grizzly bears were smaller in size and were not the livestock killers reported in historical accounts, study finds (January 10, 2024) retrieved January 10, 2024 from
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from fair use for private study or research purposes, no part may be reproduced without written permission. The content is provided for information only.