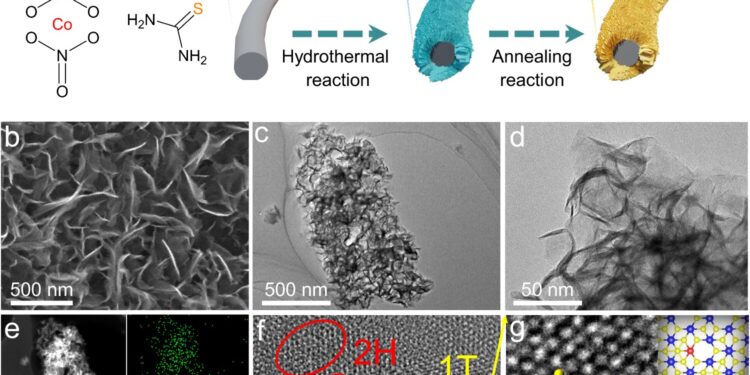
Microstructural characterizations of COITS-VS/ MOS2 Nanofeuilles. Credit: Nature communications (2025). DOI: 10.1038 / S41467-025-58273-9
A team of scientists from materials, chemical engineers and environmental scientists affiliated with a multitude of institutions in China has developed a redox flow battery (RFB) with 87.9% of energy efficiency, which can also last 850 cycles. In their project, published in the journal Nature communicationsThe group has developed a new type of catalytic electrode to improve battery efficiency.
An RFB is a type of electrochemical cell which converts chemical energy into electrical energy by reversible oxidation and the reduction of liquids at work. These batteries consist of energy storage electrolytes which are pumped through an electrochemical cell in a storage area. Because they are easily scalable, they are generally used to store large amounts of energy, such as those collected by an energy network.
However, RFBs are not effective, which is why scientists have sought ways to improve them. In this new effort, the team in China has found a way to improve efficiency using a new type of catalytic electrode.
Researchers have sought to improve the efficiency of a special RFB type called SIRFB based on polysulfure-iodide. To this end, they started with a 2D MOS2 Nanosheet and improved it with CO atoms and sulfur vacant posts, creating a new material that they described as coITS-Vs / mos2.
The new material could be used to optimize the interface, increase the absorption of reagents and accelerate the kinetics of the coupling between i–/I3– and s2-/X2-. The result was a catalytic electrode which allowed the SIRFBS in which they were put to be more effective.
Electrochemical performance of aqueous sirfbs with coITS-VS/ MOS2. Credit: Nature communications (2025). DOI: 10.1038 / S41467-025-58273-9
The tests showed the batteries capable of reaching an efficiency of 87.9% when they operate at 20 my cm-2that the research team describes as a significant improvement compared to current current Sirfbs. The battery has obtained a 95.7 MW cm cutting edge density-2 With 76.5% energy efficiency at 30 cm-2 and ran up to 50 cycles. When operated at 10 cm-2The battery has undergone stable operation at a charge state of 10% for up to 850 cycles.
The research team notes that the advanced battery efficiency could be restored by replacing the electrolytes after operating for 200 and 600 cycles.
More information:
Zhigui Wang and Al, Synergie of unique atoms and sulfur gaps for the Redox Polyulfure-Iodure Flow Battery, Nature communications (2025). DOI: 10.1038 / S41467-025-58273-9
© 2025 Science X Network
Quote: Redox Flow Battery reaches an energy efficiency of 87.9% and a longer cycling life with a new catalytic electrode (2025, April 2) recovered on April 2, 2025 from
This document is subject to copyright. In addition to any fair program for private or research purposes, no part can be reproduced without written authorization. The content is provided only for information purposes.