Johan Sandberg. Credit: Karolinska Institute
A new study from Karolinska Institutet has shown how MAIT cells, which play an important role in the body’s defense against microbes, exhibit different properties depending on the tissue in which they are located.
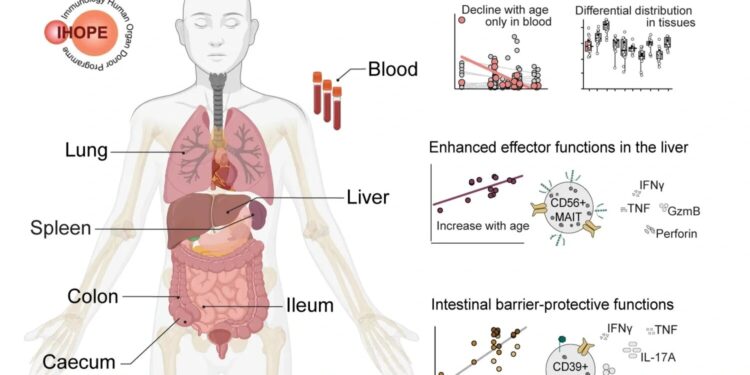
MAIT cells are a type of T cell that recognizes byproducts formed when microbes synthesize riboflavin. This makes them unique in the way they detect and fight infections. The researchers examined MAIT cells from blood samples, barrier tissues, and lymphoid tissues from organ donors to understand how these cells function in different tissues.
The results are published in the journal Sciences Immunology.
“We found that MAIT cells in the intestines have a specialized immunoregulatory profile with high expression of the regulatory enzyme CD39, suggesting that they play a role in protecting the intestinal barrier,” says Johan Sandberg, professor at the Center for Infectious Medicine (CIM), Department of Medicine, Huddinge, Karolinska Institutet.
“In the liver, on the other hand, MAIT cells mainly show high expression of the CD56 marker and an increased ability to fight microbes.”
The study also shows that the number of MAIT cells in the blood decreases with age, but is preserved in tissues. At the same time, tissue-specific functions in the intestines and liver become increasingly evident with age.
“Our results highlight the functional heterogeneity of MAIT cells and their adaptation to different tissues,” adds Professor Sandberg.
The study results add a new dimension to understanding the immune system and how different types of immune cells specialize to protect different tissues against infections.
“This allows us to better understand how this branch of the immune system works and can help us develop new treatments for infectious diseases,” says Professor Sandberg.
More information:
Tobias Kammann et al, MAIT cell heterogeneity across matched human tissues reveals specialization of distinct enhanced regulatory and effector profiles, Sciences Immunology (2024). DOI: 10.1126/sciimmunol.adn2362
Provided by the Karolinska Institute
Quote:New study reveals immune cell specialization in different tissues (2024, September 9) retrieved September 9, 2024 from
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no part may be reproduced without written permission. The content is provided for informational purposes only.