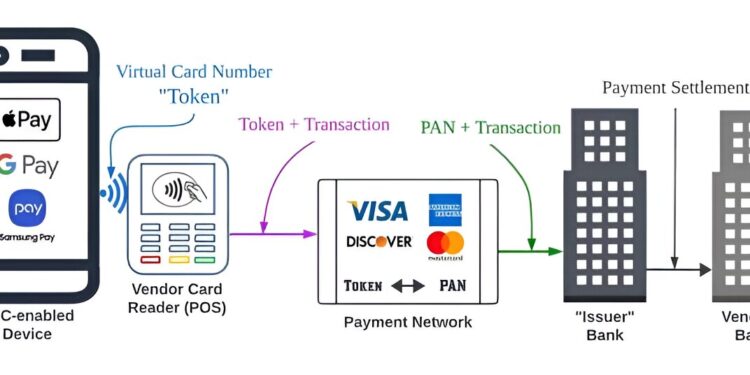
This diagram illustrates the typical environment of a digital wallet and credit card. Credit: Raja Hasnain Anwar, UMass Amherst
It’s been a week of exciting biological research: A trio of paleontologists from the University of Tsukuba, UC Berkeley, and Kyoto University have discovered evidence of a new species of extinct walrus-like mammal that once roamed the waters of the North Atlantic. The creature, called Ontocetus posti, had dietary adaptations very similar to those of the modern walrus. And a team of geneticists from RIKEN’s Center for Integrative Medical Sciences conducted an analysis of Japanese ancestry that challenges conventional theories. And a team of biologists from Western University in Canada has discovered a protein with the unique ability to stop DNA damage. Called DNA damage repair protein C, it was found in a common bacterium.
On the technical front, a team of engineers affiliated with several Chinese institutions has developed a type of smart, flexible robotic clothing intended to serve as automatic thermal adaptation in extreme heat. A group of security specialists led by a team at the University of Massachusetts Amherst has discovered a security flaw in digital wallets, even in events where the legitimate cardholder is not using a digital wallet. Additionally, a team of engineers at Sandia National Laboratories has demonstrated a quantum compass for navigation when GPS signals are unavailable. And a team of computer engineers at the Technical University of Darmstadt reports that AI models such as ChatGPT are less capable of autonomous learning than previously thought.
Separately, a team of medical researchers and geneticists from The Rockefeller University’s Developmental Neurobiology Laboratory found that knocking out a gene called Astrotactin 2 led to traits and behaviors consistent with autism in mouse models. Defects in the protein associated with the gene have been linked to neurodevelopmental problems in children. Meanwhile, cosmologist Wendy Freedman of the University of Chicago and her colleagues found that there may not be a conflict between the two methods used to measure the Hubble constant when analyzing data from the James Webb telescope. Finally, a team of medical and artificial intelligence researchers from Yale School of Medicine found that an artificial intelligence application could accurately diagnose a certain genetic disease using only facial photographs.
© 2024 Science X Network
Quote: Best of last week: Japanese ancestry questioned, digital wallet flaw, AI used to diagnose genetic diseases (2024, August 19) retrieved August 19, 2024 from
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no part may be reproduced without written permission. The content is provided for informational purposes only.